Lab IIIa
1 Introduccion
Objetivo: En este laboratorio vamos a probar diferentes librerias para graficos interactivos
2 Cargando nueva base de datos
Vamos a integrar una nueva base de datos para los movimientos de ganado bovino en el pais. Asegurate de tener la versio mas reciente de STNet instalada para acceder a los datos.
library(dplyr)
library(plotly)
library(STNet) # Cargamos la libreria
data('mov') # cargamos los datos# Primero necesitamos una tabla donde vengan las conexiones (edges)
edges <- mov %>%
select(ORIGEN, DESTINO, LONG_O, LAT_O, LONG_D, LAT_D) %>%
distinct()
# Necesitamos otra tabla que solo tenga las granjas (nodos)
nodes <- list(n1 = select(edges, ID = ORIGEN, LAT = LAT_O, LONG = LONG_O),
n2 = select(edges, ID = DESTINO, LAT = LAT_D, LONG = LONG_D)) %>%
do.call(rbind, .) %>%
count(ID, LAT, LONG)Para los siguientes mapas usaremos la libreria plotly, plotly funciona con un servicio que se llama MapBox, el cual te permite cargar mapas base para agregarlos como fondo a tus graficos. Para hacer la siguiente parte del laboratorio, es necesario tener una cuenta de MapBox
Una vez que hagas tu cuenta, puedes acceder a tu token
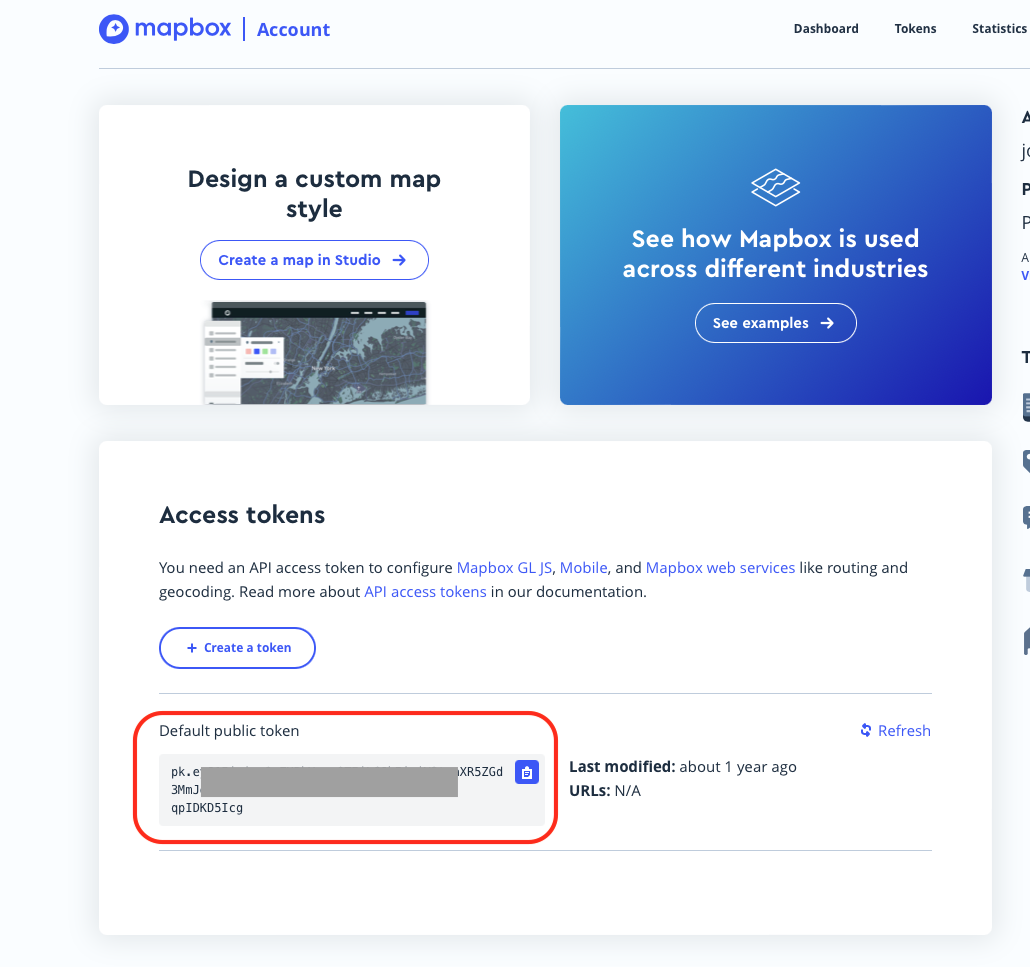
Para introducir tu token puedes usar el siguiente codigo en R
Sys.setenv('MAPBOX_TOKEN' = 'pega aqui tu token')2.1 Agregar Nodos
plot_mapbox() %>%
add_markers(data = nodes, type = 'scatter', size = ~n,
x = ~LONG, y = ~LAT, color = I('red'))2.2 Agregar segmentos
plot_mapbox() %>%
add_segments(
data = edges, alpha = 0.1, size = I(1),
x = ~LONG_O, xend = ~LONG_D,
y = ~LAT_O, yend = ~LAT_D
)3 Layout
plot_mapbox() %>%
add_segments(
data = edges, alpha = 0.1, size = I(1),
color = I('blue'),
x = ~LONG_O, xend = ~LONG_D,
y = ~LAT_O, yend = ~LAT_D
) %>%
add_markers(data = nodes, type = 'scatter', size = ~n,
x = ~LONG, y = ~LAT, color = I('red')) %>%
layout(mapbox = list(style = 'open-street-map',
center = list(lon=mean(nodes$LONG), lat=mean(nodes$LAT)),
zoom = 3))4 Integrar a la app
Ahora vamos a integrar el mapa con la aplicacion.
Primero asegurate de tener las librerias necesarias cargadas
library(shiny)
library(dplyr) # Para manipulacion de datos
library(ggplot2) # Para las figuras
library(shinydashboard) # para crear un dashboard
library(STNet)
library(sf)
library(plotly)Despues agregaremos los nuevos datos a la seccion donde los cargamos:
data('mov') # cargamos los datosDespues agregamos un nuevo tab a nuestro sidebar
sidebar <- dashboardSidebar(
sidebarMenu(
# ... Otros tabs del menu
menuItem("Movimientos", tabName = 'T4'),
# ... resto de la aplicacion
)
)Tenemos que crear un nuevo tab para este nuevo item. EN esta nueva pagina amos a crear un input para filtrar por motivo y un output para el mapa.
tabItem(tabName = 'T4',
fluidRow(
box(title = 'Motivo', width = 12,
selectInput(inputId = 'Motivo', label = 'Motivo: ',
multiple = T,
choices = unique(mov$MOTIVO),
selected = unique(mov$MOTIVO))),
box(title = 'Mapa de movimientos',
plotlyOutput('MovMap'))
)
)Ahora creamos los objetos reactivos:
# primero para filtrar los movimientos
Mov <- eventReactive(input$filter, {
mov %>%
filter(MOTIVO %in% input$Motivo,
year %in% input$year)
})
# despues para crear los edges y Nodes
edges <- eventReactive(input$filter,{
edges <- Mov() %>%
select(ORIGEN, DESTINO, LONG_O, LAT_O, LONG_D, LAT_D) %>%
distinct()
})
nodes <- list(
n1 = select(edges(), ID = ORIGEN, LAT = LAT_O, LONG = LONG_O),
n2 = select(edges(), ID = DESTINO, LAT = LAT_D, LONG = LONG_D)
) %>%
do.call(rbind, .) %>%
count(ID, LAT, LONG)Y finalmente nuestro output
output$MovMap <- renderPlotly({
plot_mapbox() %>%
add_segments(
data = edges(), alpha = 0.1, size = I(1),
color = I('blue'),
x = ~LONG_O, xend = ~LONG_D,
y = ~LAT_O, yend = ~LAT_D
) %>%
add_markers(data = nodes(), type = 'scatter',
x = ~LONG, y = ~LAT, color = I('red')) %>%
layout(mapbox = list(style = 'open-street-map',
center = list(lon=mean(nodes()$LONG), lat=mean(nodes()$LAT)),
zoom = 3))
})